What can cause a laceration wound?
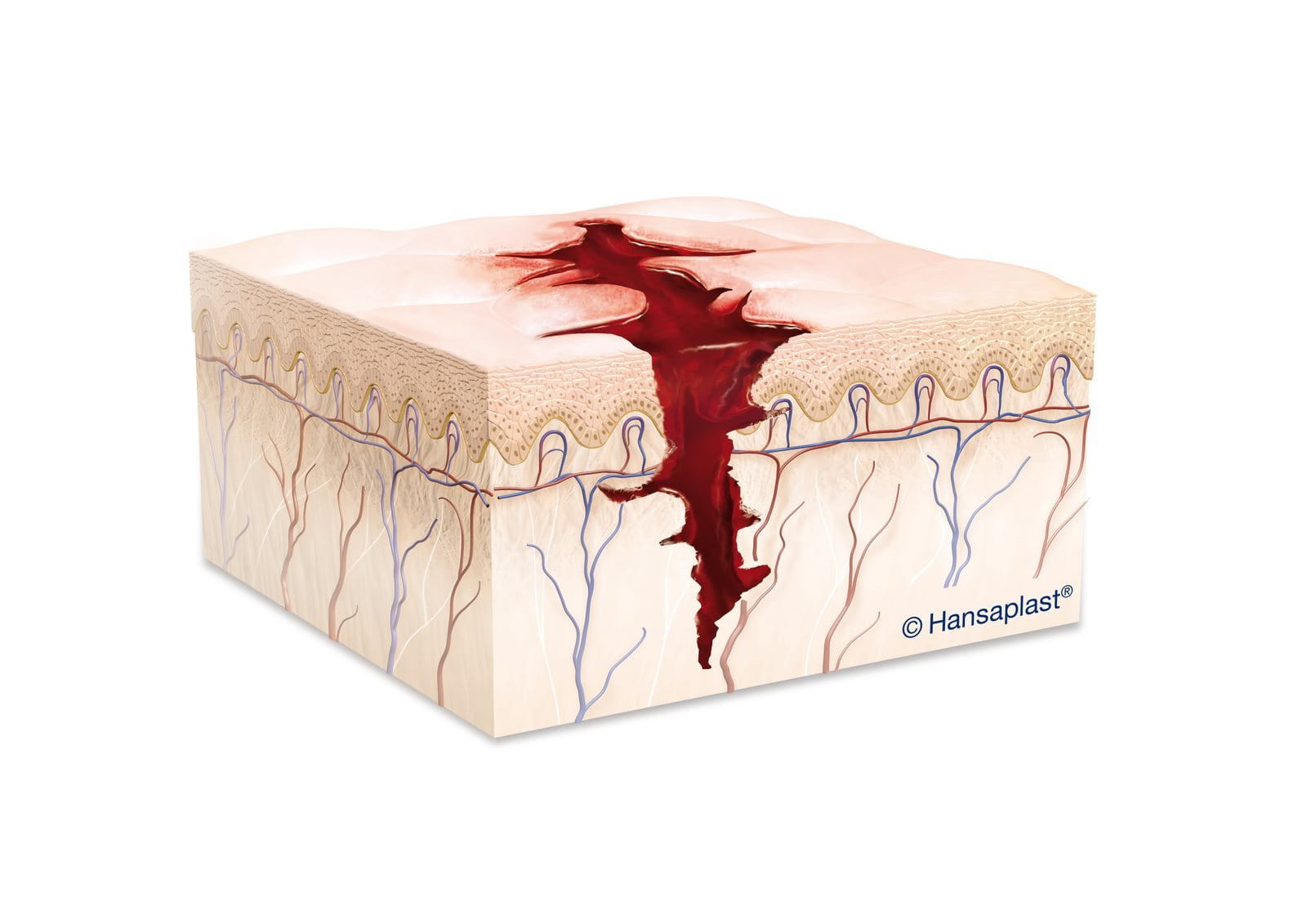
What is the difference between an abrasion and a laceration?
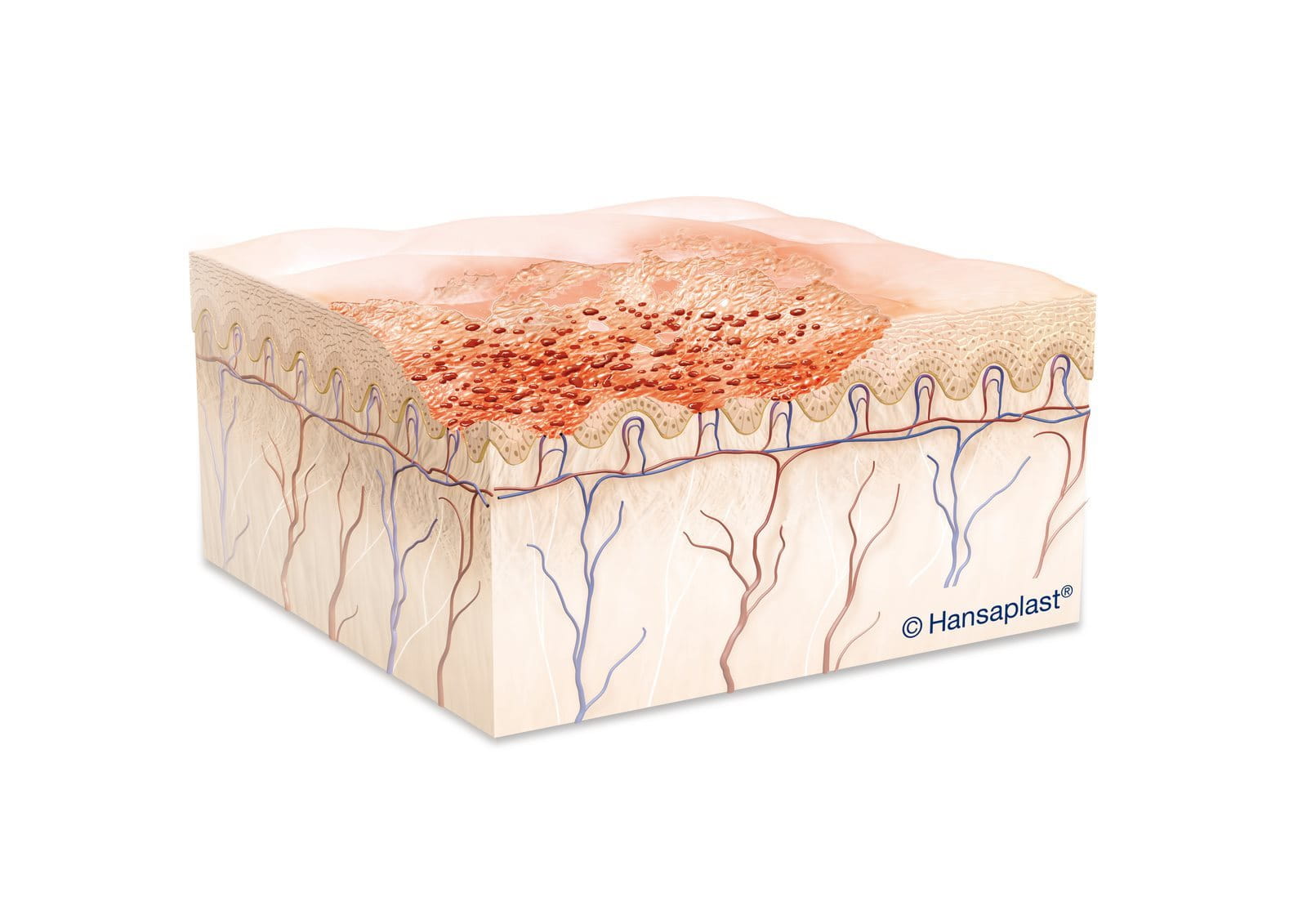
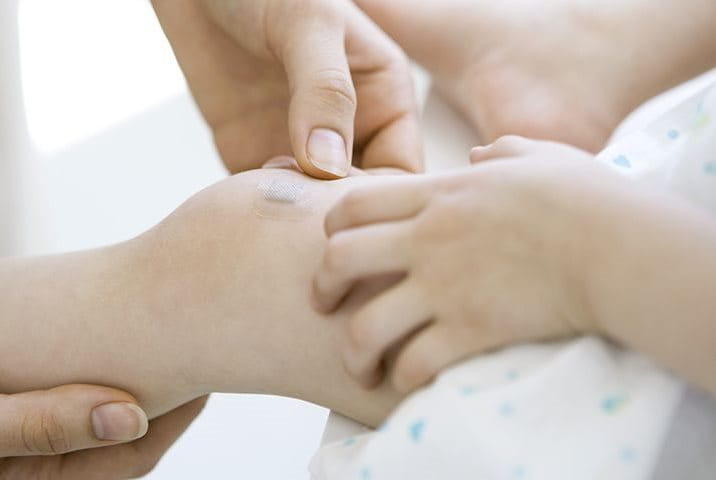
Treatment of lacerations
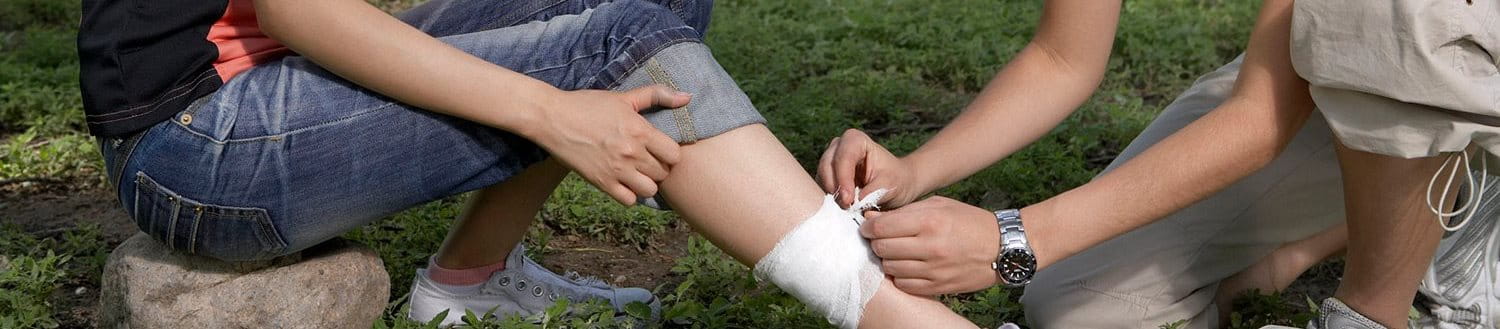
Lacerations are often severe and generally require medical attention because wide and uneven breaks in the skin lead to heavy bleeding and may require stitches.
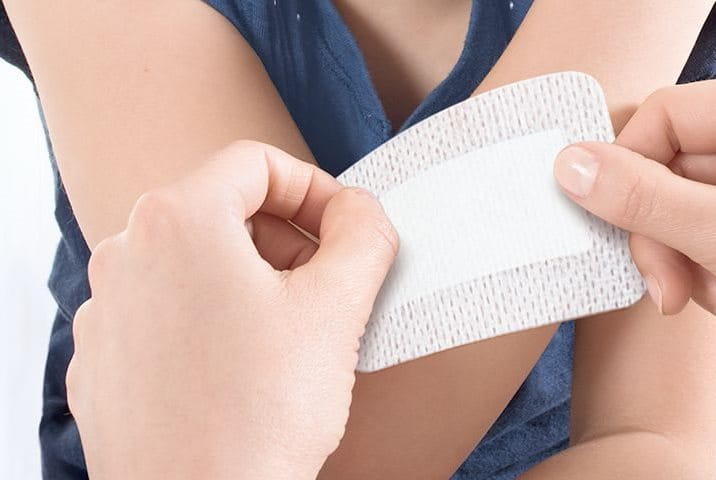
Only small, minor lacerations can be treated at home. For these wounds, follow this easy 3-step routine and heal them quickly and easily.
When do lacerations need stitches?
A healthcare professional should remove stitches and can usually be done after several days.
When to consult a medical professional

Generally, it is recommended to consult a doctor in the case of a head injury, especially for children, to ensure the best medical treatment and cosmetic results. Always take extra care during potentially dangerous activities and use protective gear such as helmets for those that pose a risk of head injury. Other instances where it is advised to seek the help of a medical professional are:
- There are signs of infection on a lacerated wound on the hand.
- There is associated cellulitis over a joint.
- There is a possible foreign body remaining in the wound after cleaning, including all injuries caused by glass.
- The laceration is complex, widely gaping, or extensively devitalised.
- There is a tetanus-prone wound, which includes wounds that require surgical intervention which has been delayed for more than six hours; wounds which have a significant degree of devitalised tissue or a puncture-type injury (particularly where there has been contact with material likely to contain tetanus spores [for example soil or manure]); wounds containing foreign bodies; compound fractures; and wounds in people who have systemic sepsis.
Head injuries